2 Which of the Following Can't Undergo Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
Which of the following aryl halides is the most reactive towards nucleophilic substitution. There are two types of mechanism for alkyl halides SN1 and SN2.
Related Videos View All Which of the following compounds does not undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions.

. Sensitive to the steric effect. Which of the following cant undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
Methyl halides are more reactive a primary compound next reactive secondary halides may react but tertiary halides are not reactive. One in which the nucleophilic attack and the. NaCN d Illustrate the mechanism for the reaction between propanone and hydrogen cyanide.
If β -hydrogen hydrogen at ortho position are absent then reaction will not take place. Q 1 c Show the mechanism for the nucleophilic substitution reaction that occurs when 2-bromopropane undergoes reflux with NaOH aqueous and name the product s formed. Aryl halides doesnt undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions under ordinary conditions because of.
Option A can not undergo nucleophilic substitution. Approach of nucleophile is retarded 2. Therefore it will not undergo nucleophilic substitution.
18 18 Which of the following cant undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions. A reaction occurs with inversion of a chiral centre. Chlorobenzene is an aryl halide and aryl halides are less reactive in comparison to alkyl halides towards either textS_textN1 or textS_textNtext2 nucleophilic substitution as the carbon halogen bond in aryl halides is strong due to stabilization by resonance and hence cannot be easily broken.
One in which the nucleophilic attack and the loss of the leaving group happen at the same time and the second in which the loss of the leaving group happens before the nucleophile can attack. At CC in the vinyl compound there is no reaction. A nucleophilic aromatic substitution is a substitution reaction in organic chemistry in which the nucleophile displaces a good leaving group such as a halide on an aromatic ringAromatic rings are usually nucleophilic but some aromatic compounds do undergo nucleophilic substitution.
Primary and secondary alkyl halides can undergo the SN2 mechanism but tertiary alkyl halides react only very slowly. I Write any two reasons for less reactivity. C Show the mechanism for the reaction below illustrating the product s formed.
The key difference is that aryl halides cannot undergo an S N 2 by a backside attack of the nucleophile and unlike S N 1 the loss of the leaving group cannot occur since the phenyl cations are very unstable. Which of the following compounds does not undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions. The mechanism of nucleophilic aromatic substitution however is different than what we learned in the S N 1 and S N 2 reactions.
While in structure III and III either hydrogen H or deuterium D is present at ortho position hence these will undergo. Hence they are not able to undergo Substitution reactions. In the case of B there is a methyl group attached to the benzene ring and the methyl group is electron-donating so the nucleophilic substitution is less.
Which of the following halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution. This molecule will undergoa bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction with hydroxide ion. When everything happens simultaneously it is called a.
These reactions are divided in two main types. The carbon-halogen bond in aryl halides has partial double bond character. The aryl halides are not capable to undergo direct nucleophilic Substitution reaction.
The substrate molecule is destabilised due to resonance 4. An sp 3 -hybridized electrophile must have a leaving group X in order for the reaction to take place. The Mechanisms of Substitution Reactions.
Approach of nucleophile is retarded. So it automatically stabilizes the carbocation. A I B 11 C III D IV E V 19 19 Which of the following alkyl bromides is likely to undergo rearangement by a 12-methyl shift.
This is because the R of halides causes a double bond between the Carbon and the halide group. Who are the experts. In the case of C there is a methoxy group and it is the strong electron-donating by R so it makes benzene electron-rich so nucleophilic attack is least favored.
Carbon carrying halogen atoms is sp3 - hybridised 3. Ethyl chloride isopropyl chloride and chloro benzene cannot undergo resonance. 2 Nucleophilic substitution is the reaction of an electron pair donor the nucleophile Nu with an electron pair acceptor the electrophile.
The bond thus gets a partial double-bond character and becomes difficult to break. A 2-bromo-33-dimethylpentane B 3-bromo-3-methylpentane C benzyl bromide D 3-bromo. In this post we will talk about the S N 2 mechanism of nucleophilic substitution reactions.
There are two main types of substitution reactions. As a reminder from the introduction to nucleophilic substitutions these are reactions where the nucleophile replaces the leaving group. Ii Give one example for nucleophilic substitution reactions of aryl halides.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. NaOH 12th attempt àl see Periodic Table O See Hint Feedback Pleasedraw all four bonds atchiral centers. In structure IV at both the ortho position methyl group CH 3.
The correct order of reactivity of the halides ethyl chloride I. View the full answer. Do halides undergo sn1.
Explanation for incorrect options. Partial double bond character between carbon and halogen. Drawthe majororganic product of that reaction including See page 407 correctstereochemistry using wedges and dashes.
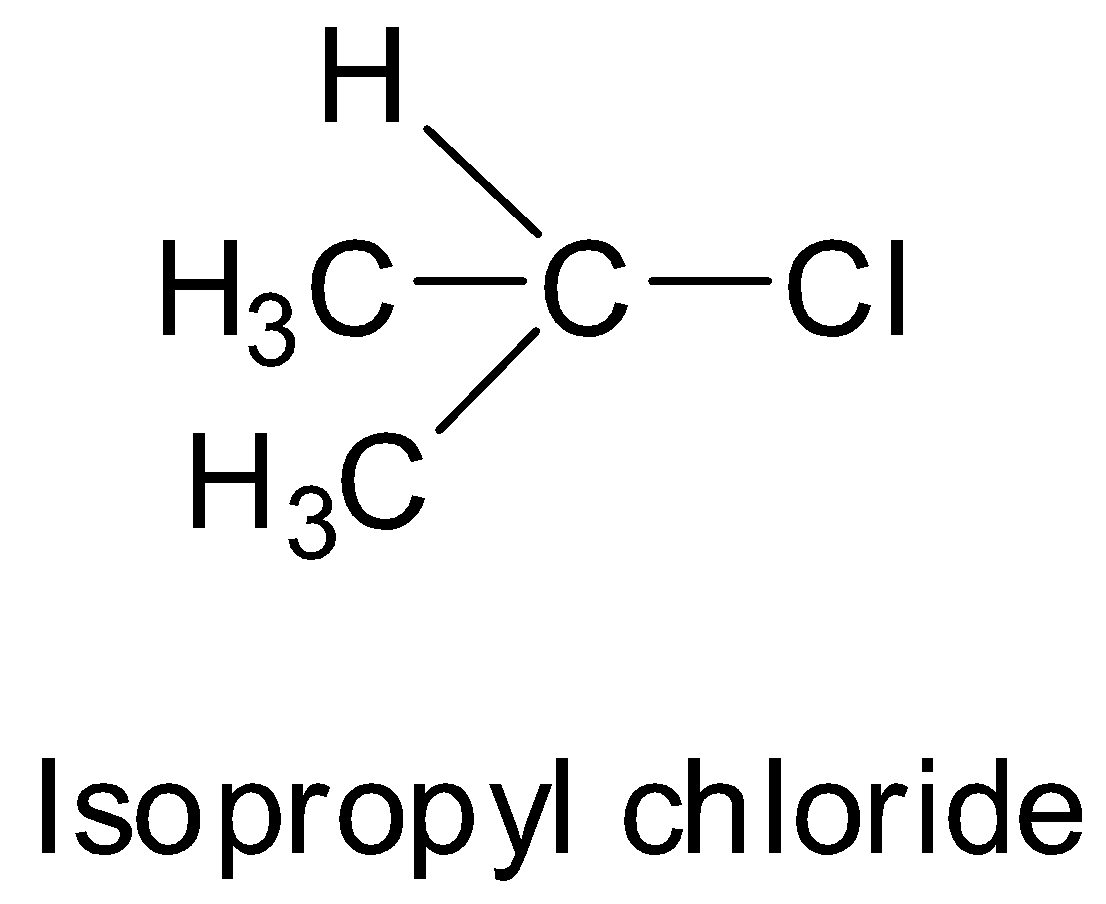
Chemistry questions and answers. A Vinyl chloride B Ethyl bromide C Benzyl chloride D Isopropyl chloride Answer A Solution As a result of resonance the carbon-chloride bond acquires some double bond character Hence vinyl chloride does not undergo nucleophilic reactions. Is attached and hydrogen is absent.
Characteristics of Nucleophilic Substitution Bimolecular Reaction. Aryl halides doesnt undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions under ordinary conditions because of 1. The SN1 mechanism is a two-stage mechanism where the first stage is the rate determining step.
Vinyl chloride does not give nucleophilic substitution reactions but allyl chloride gives. Just as normally nucleophilic alkenes can be made to undergo conjugate substitution if they. But in benzyl chloride when the chlorine leaves via nucleophilic substitution by S N 1 mechanism the carbocation formed stabilises because it undergoes resonance with the benzene ring which act as an electron group.
Aryl halides are less reactive in nucleophilic substitution reactions.

Which Of The Following Will Not Undergo Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution

Nucleophilic Attack By Donyaquick On Deviantart Chemistry Organic Chemistry Geology Humor
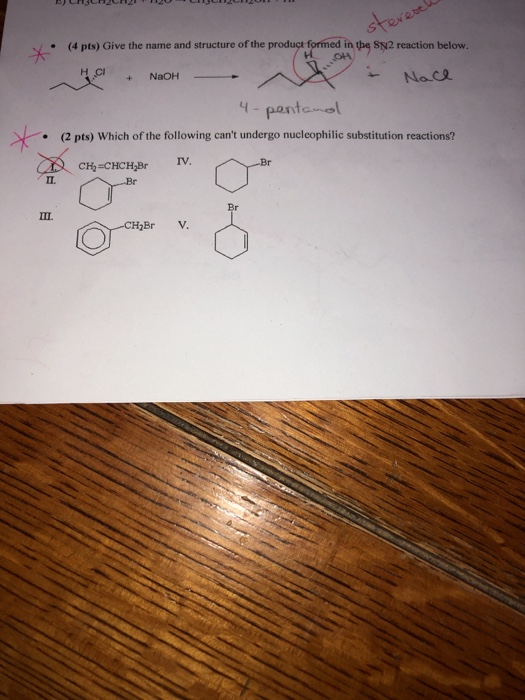
Solved 1 Give The Name And Structure Of The Product Formed Chegg Com

Which Of The Following Can Undergo Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
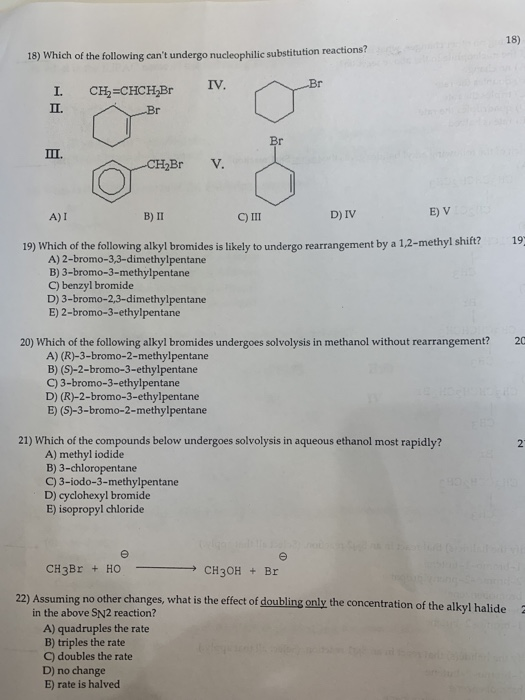
Solved 18 18 Which Of The Following Can T Undergo Chegg Com

Molecular Orbital Theory And Bond Order Molecular Electron Configuration Bond
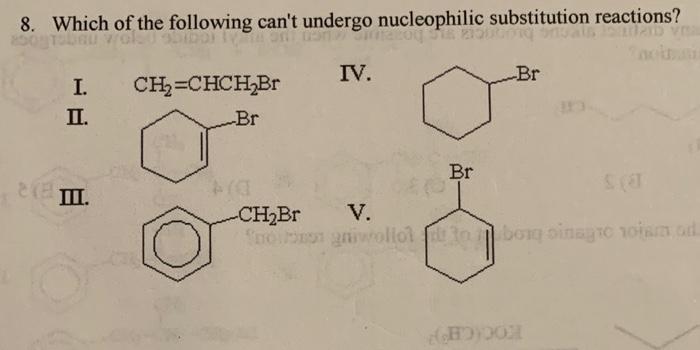
Solved 8 Which Of The Following Can T Undergo Nucleophilic Chegg Com

For The Following Compounds The Correct Statement S With Respect To Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions Is Are

Molecular Orbital Theory And Bond Order Molecular Electron Configuration Bond

Solved Which Of The Following Can T Undergo Nucleophilic Chegg Com

What Makes A Good Nucleophile 2 Teaching Chemistry Medical School Stuff Organic Chem

Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution I Video Khan Academy

The Age Of Metals I Discussed With The Help Of Chemistry I Electro Chemistry I Class 12 Youtube History Of Chemistry Chemistry Age

Banana Bond In Boron Hydrides And Cyclopropane Bond Boron Chemistry

Solved Which Of The Following Nucleophilic Substitution Chegg Com

The Age Of Metals I Discussed With The Help Of Chemistry I Electro Chemistry I Class 12 Youtube History Of Chemistry Chemistry Age
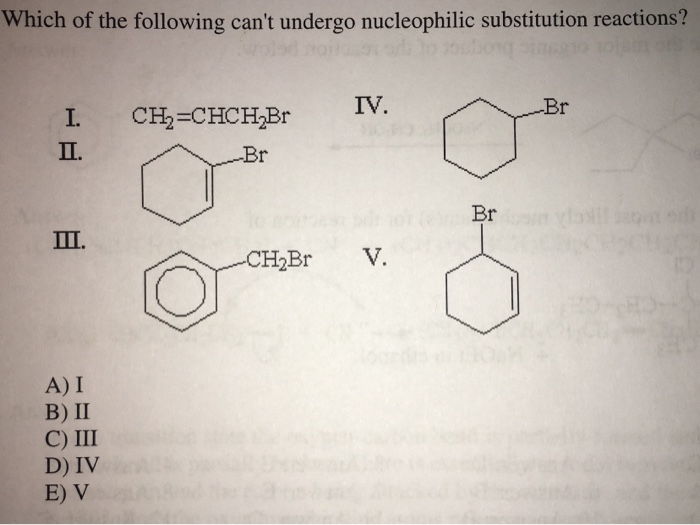
Solved Which Of The Following Can T Undergo Nucleophilic Chegg Com

Which Of The Following Compounds Does Not Undergo Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
Which Of The Following Undergoes Nucleophilic Substitution Class 11 Chemistry Cbse

Comments
Post a Comment